Indium-tin-oxide free transparent electrodes using a plasmon frequency conversion layer†
Abstract
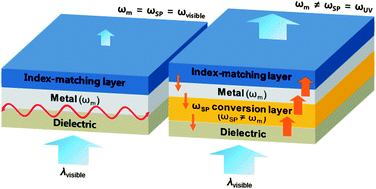
Transparent electrodes to enhance external quantum efficiency (EQE) in optoelectronic devices are proposed based on the suppression of surface plasmons (SPs) at the metal–dielectric (or metal–organic) interface using a frequency conversion layer. Plasmonic absorption at metal-based electrodes causes severe optical losses in the planar stacks of optoelectronic devices. Even though Ag is suitable for transparent electrodes owing to its lowest absorption coefficient compared to other metals, the surface plasmon resonant frequency (SPRF) of Ag is located in the visible region (i.e., ωSP ∼ 3.9 eV, λSP = 500–550 nm). Thus, incident light is absorbed by

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...