Thermoresponsive copolymer microgels
Abstract
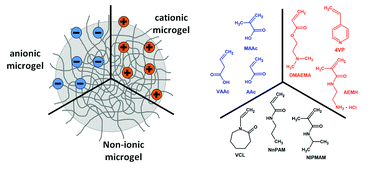
Colloidal aqueous microgels have attracted notable attention due to their possible applications in both polymer chemistry and the (bio)material sector. Due to their soft internal network structure and their response to different external stimuli, they are suitable as carrier systems for different kinds of molecules (e.g. nanoparticles, drugs, diagnostic agents, and enzymes), as optically active materials or even as model systems for fundamental research on soft condensed matter. Within the class of microgels, a variety of molecular structures is possible. The aim of this manuscript is to review recent progress in the domain of copolymer microgels with different architectures. Although most of the work is based on microgels with poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) (NIPAM) as one component, non-NIPAM based copolymer systems are also presented and discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...