Reversible bioresponsive aptamer-based nanocomposites: ATP binding and removal from DNA-grafted silica nanoparticles†
Abstract
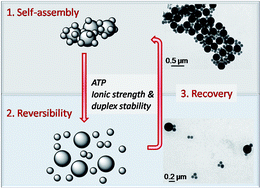
The bio-responsive reversible assembly of silica nanoparticles grafted with complementary DNA strands containing an ATP-sensitive aptamer sequence was studied. The optimal conditions for ATP-induced specific disassembly of the bionanocomposite network were identified, highlighting the existing competition between ATP/aptamer interactions and DNA duplex stability. A new, dialysis-based method for ATP removal was proposed, allowing partial re-formation of the initial DNA duplexes. Further disassembly was re-achieved by subsequent addition of ATP. These data constitute promising preliminary steps towards DNA-based fully reversible responsive bionanocomposite devices.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanoparticles in Biology

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...