Gelatin-derived nitrogen-doped porous carbon via a dual-template carbonization method for high performance supercapacitors†
Abstract
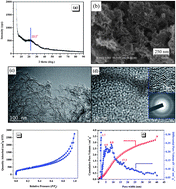
High performance nitrogen-doped porous carbon for supercapacitors, named as Gelatin–Mg–Zn-1 : 5 : 3, has been successfully prepared via a dual-template carbonization method, without any physical/chemical activation process, in which gelatin serves as both carbon/nitrogen source, and low cost Mg(NO3)2·6H2O and Zn(NO3)2·6H2O as dual templates. It is revealed that the carbonization temperature, and the mass ratio of gelatin–Mg(NO3)2·6H2O–Zn(NO3)2·6H2O plays a crucial role in the determination of surface area, pore structure and the correlative capacitive behavior of the Gelatin–Mg–Zn-1 : 5 : 3 sample. It displays a high BET surface area of 1518 m2 g−1, large total pore volume of 4.27 cm3 g−1, and large average pore width of 11.3 nm. In a three electrode system, using 6 mol L−1 KOH solution as electrolyte, we can achieve a high specific capacitance of ca. 284.1 F g−1 at a current density of 1 A g−1 and high capacitance retention of ca. 31.2% is obtained at 150 A g−1, indicating high rate capability. It also possesses a high capacitance retention of ca. 96.1% even after charging/discharging for 10 000 cycles. More importantly, a two electrode system, using [EMIm]BF4/AN (weight ratio of 1 : 1) as electrolyte, has been adopted for the Gelatin–Mg–Zn-1 : 5 : 3 sample with different operation temperatures of 25/50/80 °C. As a result, wide voltage windows, broad operation temperatures, and high cycling stability achieved in the two electrode system make it possible for practical application under extreme conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...