Novel ion-imprinted polymer using crown ether as a functional monomer for selective removal of Pb(ii) ions in real environmental water samples
Abstract
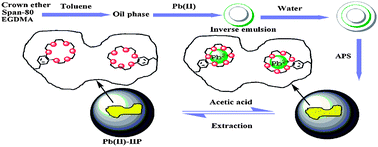
A novel Pb(II) ion-imprinted crown ether (Pb(II)-IIP) was prepared by inverse emulsion polymerization using 4-vinylbenzo-18-crown-6 as a functional monomer. Pb(II)-IIP showed higher capacity and selectivity than the non-imprinted crown ether (NIP). The monolayer adsorption capacities of Pb(II)-IIP and NIP for Pb(II) ions were 27.95 and 13.54 mg g−1, respectively. The relative selectivity coefficients of Pb(II)-IIP for Pb(II)/Zn(II), Pb(II)/Co(II), Pb(II)/Ni(II) and Pb(II)/Cd(II) were 617.79, 500.56, 52.28 and 201.15, respectively. Kinetics studies showed that the adsorption process closely agreed with a pseudo-second-order model. Pb(II)-IIP exhibited good regeneration, and the adsorption capacity of Pb(II)-IIP was stable within the first three cycles without obvious decrease. Moreover, Pb(II)-IIP showed almost 100% removal efficiency for Pb(II) ions in real environmental water samples, indicating that Pb(II)-IIP could have wide application prospects in Pb(II) removal.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...