Performance optimization of low-temperature-annealed solution-processable ZnO buffer layers for inverted polymer solar cells†
Abstract
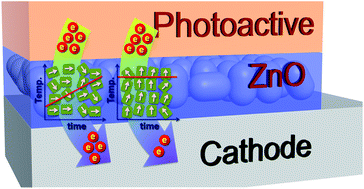
High-performance solution-processable ZnO thin films for use as electron-transporting layers (ETLs) of inverted-structured

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...