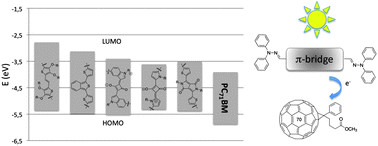
The design, synthesis and characterization of five diphenylhydrazone end capped molecules as donors for Bulk Heterojunction (BHJ) solar cells are described. The use of the hydrazone donor instead of the more common amine one is advantageous in terms of synthetic access and overall stability. We show that the variation of both the nature and the substitution pattern of the electron deficient conjugated bridge enables the tuning of the optical energy gap as well as of the HOMO and LUMO. In particular, our data show that the low energy shift of the HOMO level along the series of hydrazone compounds, one of the critical parameters affecting the performance of BHJ cells, is as high as 0.42 eV. We tested all derivatives as donors in a BHJ configuration, using the fullerene derivative [6,6]-phenyl-C71-butyric acid methyl ester (PC71BM) as the acceptor. We found that the trend we observed in the progressive stabilization of the chromophore HOMO level upon increasing the electron accepting capabilities of the conjugated bridge is reflected in the progressive increase of the cell open circuit voltage (Voc). Our preliminary results show that it is possible to obtain a Voc as high as 0.74 V, along with a power conversion efficiency of 1.2%.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...