π-Conjugated polymer–Eu3+ complexes: versatile luminescent molecular probes for temperature sensing†
Abstract
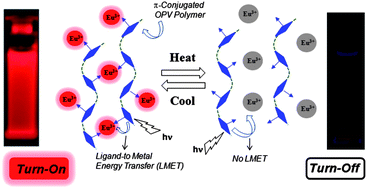
We report π-conjugated polymer–Eu3+ ion complexes as new potential luminescent thermo-sensitive molecular probes. Carboxylic acid functionalized segmented π-conjugated polymers having oligophenylenevinylene (OPV) chromophores in the poly(ethyleneoxide) or polymethylene backbones were custom designed, synthesized and utilized as efficient photosensitizers for Eu3+ ions. These π-conjugated polymer–Eu3+ ion complexes were found to be thermo-sensitive and behaved as reversible ‘turn-on’ or ‘turn-off’ luminescent switches in solution and in solid state. Luminescent decay studies revealed that the red-emission from the Eu3+ ion excited state was highly sensitive to temperature which drove the functioning of optical switches. The decay rate constants followed a typical Arrhenius trend over a wide temperature range having similar activation energies. Both the nature as well as length of the segmented polymer chain that tied the OPV optical chromophores in the backbone determine the temperature range of the luminescent on–off process. The emission characteristics of the oligomer–Eu3+ ion complex were found to be non-thermosensitive which emphasized the need for the segmented π-conjugated polymer ligand structure for the probes based on Eu3+ ion complexes. The present strategy opens up new concept and molecular design principles for π-conjugated polymer–lanthanide ion complexes as potential candidates for temperature sensitive luminescent molecular probes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...