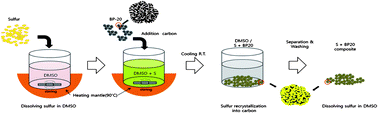
To enhance the stability of sulfur cathode for a high energy lithium–sulfur battery, sulfur–activated carbon (S–AC) composite was prepared by encapsulating sulfur into micropores of activated carbon using a solution-based processing technique. In the analysis using the prepared specimen of S–AC composite by the focused ion beam (FIB) technique, the elemental sulfur exists in a highly dispersed state inside the micropores of activated carbon, which has a large surface area and a narrow pore distribution. The S–AC composite was characterized through X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method, selected area electron diffraction (SAED), energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDX), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), thermogravimetry analysis (TGA), and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). A lithium–sulfur cell using the S–AC composite has a high first discharge capacity over 800 mA h g−1 S even at a high current density such as 2C (3200 mA g−1 S) and has good cycleability around 500 mA h g−1 S discharge capacity at the 50th cycle at the same current density.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...