Spontaneous unilamellar polymer vesicles in aqueous solution†
Abstract
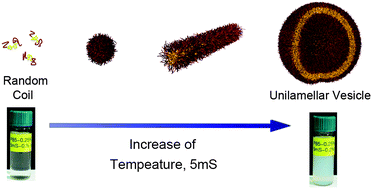
A unilamellar polymeric vesicle is a self-assembled structure of a block copolymer that forms a spherical single bilayer structure with a hydrophobic interlayer and a hydrophilic surface. Due to their enhanced colloidal stability and mechanical property, controllable surface functionality, or tunable membrane thickness, polymeric vesicles are useful in nano and bio-science, providing potential applications as nanosized carriers for catalysts, drugs, and enzymes. For fabrication of a unilamellar vesicle, however, preparative procedures with a few steps are inherently required. Herein, without complicated preparative procedures, we report spontaneous unilamellar polymeric vesicles with nanometer sizes (<100 nm), which are prepared by simply mixing a triblock copolymer, Pluronic P85 (PEO26PPO40PEO26), and an organic derivative, 5-methyl salicylic acid (5mS), in aqueous solution. Depending on the 5mS concentration and the temperature, the P85–5mS mixtures presented various self-assembled nanostructures such as spherical and cylindrical micelles or vesicles, which were characterized by small angle neutron scattering and cryo-TEM, resulting in a phase diagram drawn as a function of temperature and the 5mS concentration. Interestingly the critical temperature for the micelle-to-vesicle phase transition was easily controlled by varying the 5mS concentration, i.e. it was decreased with increasing the 5mS concentration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...