Spatially controlled apoptosis induced by released nickel(ii) within a magnetically responsive nanostructured biomaterial†
Abstract
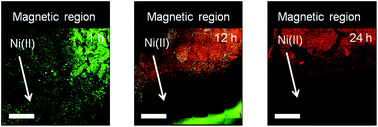
Magnetically patterned and responsive biomaterials have been shown to produce spatially controlled cell death in response to a magnetic signal. The responsive elements in these nano-structured biomaterials are magnetic

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...