Naphthalimide trifluoroacetyl acetonate: a hydrazine-selective chemodosimetric sensor†
Abstract
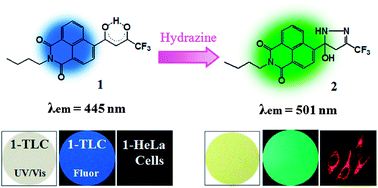
The trifluoroacetyl acetonate naphthalimide derivative 1 has been synthesized in good yield. In acetonitrile solution, compound 1 reacts selectively with hydrazine (NH2NH2) to give a five-membered ring. This leads to OFF–ON fluorescence with a maximum intensity at 501 nm as well as easily discernible color changes. Based on a readily discernible and reproducible 3.9% change in overall fluorescence intensity, the limit of detection for 1 is 3.2 ppb (0.1 μM), which is below the accepted limit for hydrazine set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Compound 1 is selective for hydrazine over other amines, including NH4OH, NH2OH, ethylenediamine, methylamine, n-butylamine, piperazine, dimethylamine, triethylamine, pyridine, and is not perturbed by environmentally abundant metal ions. When supported on glass-backed silica gel TLC plates, compound 1 acts as a fluorimetric and colorimetric probe for hydrazine vapor at a partial pressure of 9.0 mm Hg, with selectivity over other potentially interfering volatile analytes, including ammonia, methylamine, n-butylamine, formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, H2O2, HCl, and CO2 being observed. Probe 1 can also be used for the detection of hydrazine in HeLa cells and does so without appreciable interference from other biologically abundant amines and metal ions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...