Helical self-assembly and nonlinear optical properties of optically active phthalocyanine derivatives bearing eight optically active diethyleneglycol mono-(S)-2-methylbutyl ether moieties on the β-position of the phthalocyanine ring†
Abstract
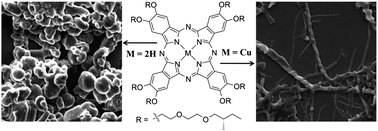
Two phthalocyanine derivatives with eight peripheral chiral diethyleneglycol mono-(S)-2-methylbutyl ether moieties on the β-position of the phthalocyanine ring were prepared from the tetramerization of corresponding phthalonitriles, promoted by organic base 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU). The self-assembly behavior of metal free phthalocyanine 1 and its copper congener 2 have been comparatively investigated by electronic absorption and circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The metal free phthalocyanine 1 self-assembles into the right-handed screw-like aggregates (ca. 10 μm length, 6 μm width, and 1.5 μm helical pitch), while, phthalocyaninato copper 2 self-assembled into left-handed fibrous aggregates (ca. 25 μm length, 1 μm width, and 0.7 μm helical pitch). These results indicated the effect of metal-coordination bonds on the morphology and handedness of the self-assembled nanostructures. Further, excellent nonlinear optical (NLO) properties of both compounds were also revealed by a Z-scan experiment, which expand their applications in nonlinear optics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...