Synthesis and characterization of polyaniline nanoparticles with enhanced microwave absorption†
Abstract
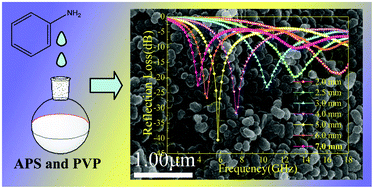
A series of polyaniline (PANI) materials have been prepared by a reverse dropping method with the assistance of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP). It can be found that PVP and the dropping rate play critical roles in determining the morphology evolution of PANI, and the restriction of PVP is highly dependent on the dropping rate. Well dispersed PANI nanoparticles can only be obtained under moderate conditions. Thanks to the unique preparative process, these samples show significant changes in the length and oxidation state of conjugated chains, as proved by the results of UV/vis absorption spectra and FT-IR spectra, which result in their distinguishable conductivity and microwave absorption. Very interestingly, PANI nanoparticles exhibit substantially enhanced microwave absorption properties. In particular the optimum one, PANI-NP2, presents very strong reflection loss (−40.5 dB at 5.8 GHz) and wide response bandwidth (3.2–18 GHz over −10 dB), which are indeed comparable to those composites of PANI with various magnetic particles, implying promising applications as a kind of light-weight and highly effective microwave absorber. By systematically investigating the electromagnetic parameters, it can be concluded that suitable complex permittivity, improved characteristic impedance and multiple relaxation processes in PANI nanoparticles should be responsible for their good microwave absorption.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...