Thiophene based hyperbranched polymers with tunable branching using direct arylation methods†
Abstract
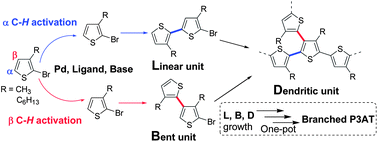
An efficient one-pot synthesis of branched poly(3-alkylthiophene)s (b-P3ATs) is achieved via a dehydrohalogenative polycondensation reaction. The structures of the b-P3ATs are assigned based on

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...