Effects of poly(vinyl pivalate)-based stabiliser architecture on CO2-solubility and stabilising ability in dispersion polymerisation of N-vinyl pyrrolidone†
Abstract
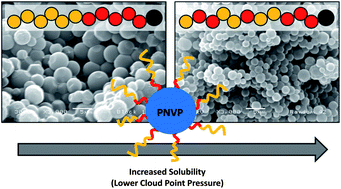
We report the comparison of block and
* Corresponding authors
a
School of Chemistry, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK
E-mail:
steve.howdle@nottingham.ac.uk
Tel: +44 (0)1159513486
We report the comparison of block and

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
N. A. Birkin, O. J. Wildig and S. M. Howdle, Polym. Chem., 2013, 4, 3791 DOI: 10.1039/C3PY00275F
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence. You can use material from this article in other publications without requesting further permissions from the RSC, provided that the correct acknowledgement is given.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
