Disulfide bond reduction-triggered molecular hydrogels of folic acid–Taxol conjugates†
Abstract
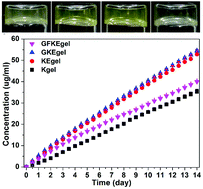
Molecular hydrogels of therapeutic agents are a novel kind of self-delivery system that can sustain release of drugs or pro-drugs. We have previously developed a molecular hydrogelator of folic acid (FA)–Taxol conjugate triggered by phosphatase. In this paper, we report a novel molecular hydrogelator system of FA–Taxol conjugates with improved synthetic strategy. The hydrogels are formed by the reduction of disulfide bond by glutathione (GSH). These hydrogels could sustain release of Taxol through ester bond hydrolysis. Compared with intravenous (i.v.) injection of clinically used Taxol® with four times the dosage, our hydrogel could inhibit tumor growth more efficiently by a single dose of intra-tumor (i.t.) administration. These observations suggested the big potential of this novel gelation system of Taxol for cancer therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...