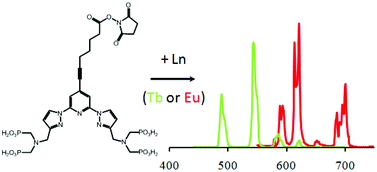
The first example of an activated phosphonated trifunctional chelate (TFC) is presented, which combines a non-macrocyclic coordination site for lanthanide coordination based on two aminobis-methylphosphonate coordinating arms, a central bispyrazolylpyridyl antenna and an N-hydroxysuccinimide ester in para position of the central pyridine as an activated function for the labeling of biomaterial. The synthesis of the TFC is presented together with photo-physical studies of the related Tb and Eu complexes. Excited state lifetime measurements in H2O and D2O confirmed an excellent shielding of the cation from water molecules with a hydration number of zero. The Tb complex provides a high photoluminescence (PL) quantum yield of 24% in aqueous solutions (0.01 M Tris–HCl, pH 7.4) and a very long luminescence lifetime of 2.6 ms. The activated ligand was conjugated to different biological compounds such as streptavidin, and a monoclonal antibody against total prostate specific antigen (TPSA). In combination with AlexaFluor647 (AF647) and crosslinked allophycocyanin (XL665) antibody (ABs) conjugates, homogeneous time-resolved Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) immunoassays of TPSA were performed in serum samples. The Tb donor–dye acceptor FRET pairs provided large Förster distances of 5.3 nm (AF647) and 7.1 nm (XL665). A detailed time-resolved FRET analysis of Tb donor and dye acceptor PL decays revealed average donor–acceptor distances of 4.2 nm (AF647) and 6.3 nm (XL665) within the sandwich immunocomplex and FRET efficiencies of 0.79 and 0.68, respectively. Very low detection limits of 1.4 ng mL−1 (43 pM) and 2.4 ng mL−1 (74 pM) TPSA were determined using a KRYPTOR fluorescence immunoanalyzer. These results demonstrate the applicability of our novel Tb-bioconjugates for highly sensitive clinical diagnostics.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...