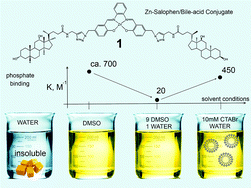
Receptor 1, composed of two deoxycholic acid moieties appended to a Zn–salophen complex, was prepared, characterized and tested for anion binding by 1H NMR and UV-vis spectroscopic techniques. While in polar DMSO, 1 is able to bind phosphate (K = ∼700 M−1), the addition of water severely diminishes the association. In a 1 : 9 water–DMSO mixture, the binding constant K is only ca. 20 M−1. Notably, in an aqueous solution of CTABr micelles (CTABr 10 mM, cmc = ∼1 mM), the zinc–salophen conjugate 1, due to its two non-polar bile-acid moieties, becomes solubilized and, most importantly, it almost completely recovers its binding ability towards phosphate, displaying a remarkable affinity (K = ∼450 M−1) in water.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...