Nanoscopic polypyrrole AFM–SECM probes enabling force measurements under potential control†
Abstract
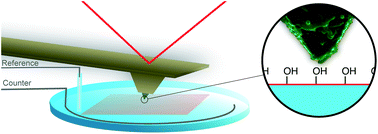
Conductive polymers, and in particular polypyrrole, are frequently used as biomimetic interfaces facilitating growth and/or differentiation of cells and tissues. Hence, studying forces and local interactions between such polymer interfaces and cells at the nanoscale is of particular interest. Frequently, such force interactions are not directly accessible with high spatial resolution. Consequently, we have developed nanoscopic polypyrrole electrodes, which are integrated in AFM-SECM probes. Bifunctional AFM-SECM probes were modified via ion beam-induced deposition resulting in pyramidal conductive Pt–C composite electrodes. These nanoscopic electrodes then enabled localized polypyrrole deposition, thus resulting in polymer-modified AFM probes with a well-defined geometry. Furthermore, such probes may be reversibly switched from an insulating to a conductive state. In addition, the hydrophilicity of such polymer tips is dependent on the dopant, and hence, on the oxidation state. Force studies applying different tip potentials were performed at plasma-treated glass surfaces providing localized information on the associated force interactions, which are dependent on the applied potential and the dopant.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...