SBA-15 confined synthesis of TiNb2O7 nanoparticles for lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
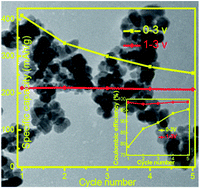
Unlike most conventional anode materials, the newly developed TiNb2O7 (TNO) does not form a solid electrolyte interface (SEI) layer, which makes it safe for high power requiring lithium-ion batteries. In this paper, we demonstrated an SBA-15 confined synthetic approach to prepare TNO nanoparticles (S-TNO) with a small particle size around 10 nm and a large BET surface area of 79.5 m2 g−1. It is worth mentioning that this is the smallest size reported so far for TNO. In contrast, the TNO (L-TNO) synthesized without SBA-15 has a particle size above 100 nm and a BET surface area of only 4.3 m2 g−1. The S-TNO shows better lithium-ion storage properties than L-TNO. The excellent electrochemical performance of S-TNO is attributed to its small crystalline size, which not only provides a larger effective area for better contact between the electrode material and the electrolyte, but also reduces the rate-limiting Li diffusion path. Moreover, S-TNO shows a high Coulombic efficiency (above 98% over 300 cycles) and negligible increase of impedance after cycling, which confirms no SEI layer formation in the operational voltage (1–3 V) of TNO.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...