Lipid-insertion enables targeting functionalization of erythrocyte membrane-cloaked nanoparticles†
Abstract
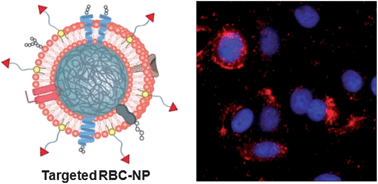
RBC membrane-cloaked polymeric
* Corresponding authors
a
Department of NanoEngineering, University of California, San Diego, 9500 Gilman Drive, La Jolla, CA 92093, USA
E-mail:
zhang@ucsd.edu
Tel: +1-858-246-0999
b Moores Cancer Center, University of California, San Diego, 9500 Gilman Drive, La Jolla, CA 92093, USA
c Department of Bioengineering, University of California, San Diego, 9500 Gilman Drive, La Jolla, CA 92093, USA
d Department of Pediatric Research, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX 77030, USA
e Key Laboratory of Smart Drug Delivery, Ministry of Education & PLA, School of Pharmacy, Fudan University, Shanghai 201203, China
RBC membrane-cloaked polymeric

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
R. H. Fang, C. J. Hu, K. N. H. Chen, B. T. Luk, C. W. Carpenter, W. Gao, S. Li, D. Zhang, W. Lu and L. Zhang, Nanoscale, 2013, 5, 8884 DOI: 10.1039/C3NR03064D
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence. You can use material from this article in other publications without requesting further permissions from the RSC, provided that the correct acknowledgement is given.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
