Yeast-based genome mining, production and mechanistic studies of the biosynthesis of fungal polyketide and peptide natural products
Abstract
Covering: up to November 2012
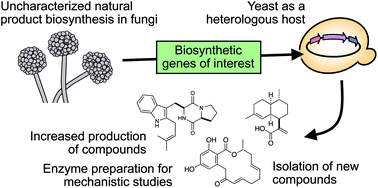
In this article, we review recent successful efforts to engineer biosynthesis of several important fungal natural products through heterologous expression of relevant biosynthetic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We also describe an innovative method of rapidly cloning fungal polyketide synthase or nonribosomal peptide synthetase genes, which can be 5–20 kb or longer, from a pool of total RNA obtained from the fungus of interest using the technique we termed the “overlap extension PCR-yeast homologous recombination (ExRec)” method. The process concomitantly incorporates the cloned genes into yeast expression vectors for biosynthesis of corresponding polyketide and nonribosomal peptide compounds in our engineered S. cerevisiae strain, allowing detailed chemical characterizations to identify the activities of those previously uncharacterized biosynthetic megaenzymes. Studies reviewed here highlight yeast as a useful and versatile host not only for production of various natural products and mechanistic investigation of biosynthetic enzymes, but also for mining of uncharacterized fungal genomes for novel secondary metabolite biosynthetic pathways.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...