Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of benzylamine supported platinum(iv) complexes†
Abstract
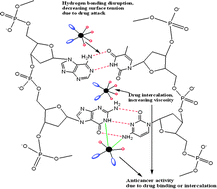
A series of benzylamine derivative (BAD) supported platinum(IV) complexes (PtCl4(BADs)2) have been synthesized. The complexes were tested in vitro against the MCF-7 cell line, and the 4-fluoro and 4-chloro containing complexes expressed impressive anticancer activities. Their DNA binding nature for a structure–activity relationship (SAR) study was investigated with physicochemical-indicators (PCI) which categorized them as good intercalators for host–guest chemistry. A mechanism for drug efficacy is proposed by analysis of the resultant viscosity and surface tension of PtCl4(BADs)2–DNA solutions named as the drug-friccohesity interaction (DFI). The complexes have shown significant antioxidant activity, determined on the basis of free radical scavenging effects due to their terminating action against the reactive species.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...