Exceptionally strong intermolecular association in hydrophobic DNA minor groove binders and their potential therapeutic consequences†
Abstract
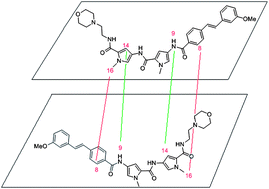
An antibacterial DNA minor groove binder is shown by NOE experiments to self-associate in aqueous solution at temperatures up to 80 °C in an anti-parallel, head-to-tail orientation as found in binding to duplex DNA oligomers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...