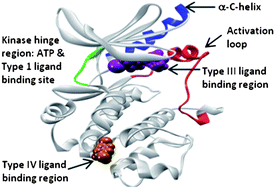
The catalytic domain of kinases shows a high degree of sequence homology, especially for kinases that belong to the same family. They share a common ATP binding site with a conserved activation loop and similar three-dimensional structure. Consequently, a major challenge in kinase research exists in achieving selectivity among the >500 family members, since they all process the same substrate. In addition to requiring selectivity against other kinases, ATP site inhibitors must also bind tightly to overcome the high physiological concentration of ATP in the cell. Furthermore, the development of novel ATP site inhibitors is becoming increasingly challenging, as many ATP competitive scaffolds have previously been disclosed. In order to develop compounds with better selectivity among kinases, inhibitors that bind outside the ATP site show great promise and are currently being explored by many groups. This review will highlight the most commonly used methods to discover small molecule Type III and IV kinase inhibitors.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...