The metabolic disturbances of isoproterenol induced myocardial infarction in rats based on a tissue targeted metabonomics†
Abstract
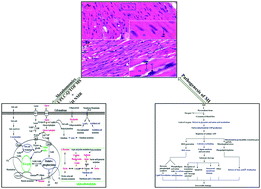
Myocardial infarction (MI) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality but the precise mechanism of its pathogenesis remains obscure. To achieve the most comprehensive screening of the entire metabolome related to isoproterenol (ISO) induced-MI, we present a tissue targeted metabonomic study using an integrated approach of ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q/TOF MS) and proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR). Twenty-two metabolites were detected as potential biomarkers related to the formation of MI, and the levels of pantothenic acid (2), lysoPC(18:0) (4), PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:0) (5), taurine (6), lysoPC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (9), threonine (12), alanine (13), creatine (14), phosphocreatine (15), glucose 1-phosphate (17), glycine (19), xanthosine (20), creatinine (21) and glucose (22) were decreased significantly, while the concentrations of histamine (1), L-palmitoylcarnitine (3), GSSG (7), inosine (8), arachidonic acid (10), linoelaidic acid (11), 3-methylhistamine (16) and glycylproline (18) were increased significantly in the MI rats compared with the control group. The identified potential biomarkers were involved in twelve metabolic pathways and achieved the most entire metabolome contributing to the injury of the myocardial tissue. Five pathways, including taurine and hypotaurine metabolism, glycolysis, arachidonic acid metabolism, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism and histidine metabolism, were significantly influenced by ISO-treatment according to MetPA analysis and suggested that the most prominent changes included inflammation, interference of calcium dynamics, as well as alterations of energy metabolism in the pathophysiologic process of MI. These findings provided a unique perspective on localized metabolic information of ISO induced-MI, which gave us new insights into the pathogenesis of MI, discovery of targets for clinical diagnosis and treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...