Identification of microRNA and bioinformatics target gene analysis in beef cattle intramuscular fat and subcutaneous fat†
Abstract
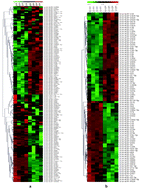
MicroRNA (miRNA) is endogenous non-coding RNA that has been proposed to play an important role in the formation of body fat. However, the differential expression of miRNA and the role of these miRNAs in bovine intramuscular and subcutaneous fat tissue are still unknown. In this study, the profile of differentially expressed miRNA and the target gene analysis in intramuscular adipose and subcutaneous adipose of adult beef cattle were investigated by microarray and bioinformatics. The data identified 88 differentially expressed miRNAs in 213 miRNAs which were detected on the microarray, and 30 miRNAs among these 88 miRNAs were changed significantly between intramuscular and subcutaneous fat (fold change >1, P < 0.001). miR-143, miR-145, miR-26a, miR-2373-5p and miR-23b-3p were highly expressed in intramuscular fat, whilst miR-26a, miR-2373-5p, miR-2325c, miR-3613 and miR-2361 showed highest abundance in subcutaneous fat. Bioinformatics of KEGG pathway analysis and GO term enrichment suggested that these differentially expressed miRNAs involved in different pathways and target genes may regulate differently the fat deposition. Taken together, our study provides the first evidence for better understanding the differential expression and mechanisms of miRNA in bovine fat deposition, and provides thinking to improve the quality of beef by reducing subcutaneous fat and increasing intramuscular fat of beef cattle.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...