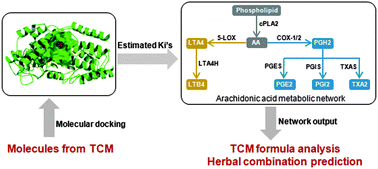
Understanding traditional Chinese medicine anti-inflammatory herbal formulae by simulating their regulatory functions in the human arachidonic acid metabolic network†
Abstract
Through history, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has adopted oriental philosophical practices of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...