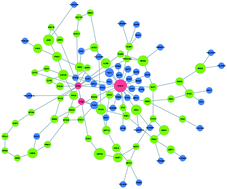
Large scale screening experiments have become the workhorse of molecular biology, producing data at an ever increasing scale. The interpretation of such data, particularly in the context of a protein interaction network, has the potential to shed light on the molecular pathways underlying the phenotype or the process in question. A host of approaches have been developed in recent years to tackle this reconstruction challenge. These approaches aim to infer a compact subnetwork that connects the genes revealed by the screen while optimizing local (individual path lengths) or global (likelihood) aspects of the subnetwork. Yosef et al. [Mol. Syst. Biol., 2009, 5, 248] were the first to provide a joint optimization of both criteria, albeit approximate in nature. Here we devise an integer linear programming formulation for the joint optimization problem, allowing us to solve it to optimality in minutes on current networks. We apply our algorithm, iPoint, to various data sets in yeast and human and evaluate its performance against state-of-the-art algorithms. We show that iPoint attains very compact and accurate solutions that outperform previous network inference algorithms with respect to their local and global attributes, their consistency across multiple experiments targeting the same pathway, and their agreement with current biological knowledge.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...