Prediction of active sites of enzymes by maximum relevance minimum redundancy (mRMR) feature selection†
Abstract
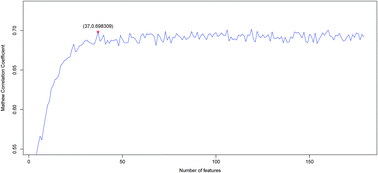
Identification of catalytic residues plays a key role in understanding how enzymes work. Although numerous computational methods have been developed to predict catalytic residues and active sites, the prediction accuracy remains relatively low with high false positives. In this work, we developed a novel predictor based on the Random Forest algorithm (RF) aided by the maximum relevance minimum redundancy (mRMR) method and incremental feature selection (IFS). We incorporated features of physicochemical/biochemical properties, sequence conservation, residual disorder, secondary structure and

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...