Size-selective collection of circulating tumor cells using Vortex technology†
Abstract
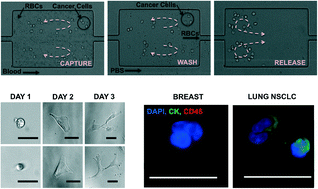
A blood-based, low cost alternative to radiation intensive CT and PET imaging is critically needed for cancer prognosis and management of its treatment. “Liquid biopsies” of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from a relatively non-invasive blood draw are particularly ideal, as they can be repeated regularly to provide up to date molecular information about the cancer, which would also open up key opportunities for personalized therapies. Beyond solely diagnostic applications, CTCs are also a subject of interest for drug development and cancer research. In this paper, we adapt a technology previously introduced, combining the use of micro-scale vortices and inertial focusing, specifically for the high-purity extraction of CTCs from blood samples. First, we systematically varied parameters including channel dimensions and flow rates to arrive at an optimal device for maximum trapping efficiency and purity. Second, we validated the final device for capture of cancer cell lines in blood, considering several factors, including the effect of blood dilution, red blood cell lysis and cell deformability, while demonstrating cell viability and independence on EpCAM expression. Finally, as a proof-of-concept, CTCs were successfully extracted and enumerated from the blood of patients with breast (N = 4, 25–51 CTCs per 7.5 mL) and lung cancer (N = 8, 23–317 CTCs per 7.5 mL). Importantly, samples were highly pure with limited leukocyte contamination (purity 57–94%). This Vortex approach offers significant advantages over existing technologies, especially in terms of processing time (20 min for 7.5 mL of whole blood), sample concentration (collecting cells in a small volume down to 300 μL), applicability to various cancer types, cell integrity and purity. We anticipate that its simplicity will aid widespread adoption by clinicians and biologists who desire to not only enumerate CTCs, but also uncover new CTC biology, such as unique gene mutations, vesicle secretion and roles in metastatic processes.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Circulating Tumor Cells

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...