Engineering of functional, perfusable 3D microvascular networks on a chip†
Abstract
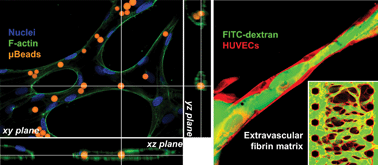
Generating perfusable 3D microvessels in vitro is an important goal for tissue engineering, as well as for reliable modelling of blood vessel function. To date, in vitro blood vessel models have not been able to accurately reproduce the dynamics and responses of endothelial cells to grow perfusable and functional 3D vascular networks. Here we describe a microfluidic-based platform whereby we model natural cellular programs found during normal development and angiogenesis to form perfusable networks of intact 3D microvessels as well as tumor vasculatures based on the spatially controlled co-culture of endothelial cells with stromal fibroblasts, pericytes or cancer cells. The microvessels possess the characteristic morphological and biochemical markers of in vivo blood vessels, and exhibit strong barrier function and long-term stability. An open, unobstructed microvasculature allows the delivery of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...