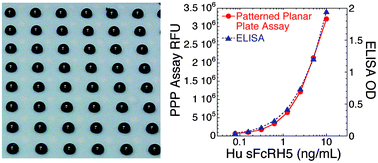
Miniaturization of immunoassays has numerous potential advantages over traditional ELISAs. Here we present a novel approach using patterned planar plates (PPPs). These ‘wall-less’ plates consist of a 16 × 24 array of 2 mm diameter hydrophilic regions surrounded by a hydrophobic polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) coating. Assays are performed by adding 2 μL droplets to the hydrophilic areas. These droplets are overlaid with an immiscible mixture of perfluorocarbon liquid (PFCL) that essentially eliminates evaporation. During wash steps, a thin film of PFCL covers the hydrophobic coating and prevents its wetting by wash buffer; as a result, the hydrophilic wells remain intact and inter-well cross-contamination is prevented. We compared the performance of three immunoassays using PPPs versus traditional 384-well ELISA plates. These included assays for soluble FcRH5 in human serum, SDF-1 in mouse serum, and human IgG in mouse plasma. The results show that the PPP assays were closely comparable to the ELISAs in terms of sensitivity, linearity of dilution, and sample quantitation. Moreover, the PPP assays were rapid to perform, easily adapted from ELISA protocols, and used 10- to 50-fold less sample and reagent volume as compared to 384- or 96-well plate ELISAs. As an additional advantage, PPPs conform to established microplate dimensional standards making them compatible with pre-existing equipment and workflows. PPPs therefore represent an attractive and broadly applicable approach to flexible miniaturization of plate-based immunochemical assays.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...