A microfluidic microelectrode array for simultaneous electrophysiology, chemical stimulation, and imaging of brain slices†
Abstract
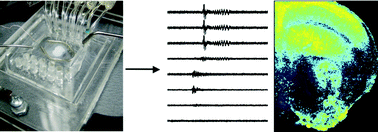
In order to understand information processing in neural circuits, it is necessary to detect both electrical and chemical signaling with high spatial and temporal resolution. Although the primary currency of neural information processing is electrical, many of the downstream effects of the electrical signals on the circuits that generate them are dependent on activity-dependent increases in intracellular calcium concentration. It is therefore of great utility to be able to record electrical signals in neural circuits at multiple sites, while at the same time detecting optical signals from reporters of intracellular calcium levels. We describe here a microfluidic multi-

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...