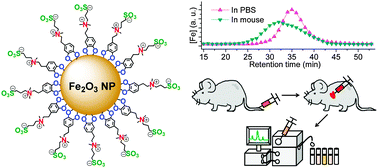
We have recently developed compact and water-soluble zwitterionic dopamine sulfonate (ZDS) ligand coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) for use in various biomedical applications. The defining characteristics of ZDS-coated SPIONs are small hydrodynamic diameters, low non-specific interactions with fetal bovine serum, the opportunity for specific labeling, and stability with respect to time, pH, and salinity. We report here on the magnetic characterization of ZDS-coated SPIONs and their in vitro and in vivo performance relative to non-specific interactions with HeLa cells and in mice, respectively. ZDS-coated SPIONs retained the superparamagnetism and saturation magnetization (Ms) of as-synthesized hydrophobic SPIONs, with Ms = 74 emu g−1 [Fe]. Moreover, ZDS-coated SPIONs showed only small non-specific uptake into HeLa cancer cells in vitro and low non-specific binding to serum proteins in vivo in mice.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...