Starch aerogel beads obtained from inclusion complexes prepared from high amylose starch and sodium palmitate
Abstract
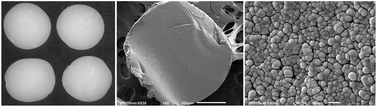
Starch aerogels are a class of low density, highly porous, renewable materials currently prepared exclusively from retrograded starch gels and are of interest due to their high surface area, porosity, biocompatibility, and biodegradability. Recently, we have reported the preparation and properties of amylose-fatty acid salt helical inclusion complexes prepared by steam jet-cooking amylose-containing starches and then blending the resulting dispersions with sodium palmitate. Dispersions of these amylose-sodium palmitate complexes prevent amylose from retrograding and possess polyelectrolyte properties due to the anionic charge of the sodium palmitate. Stable aqueous dispersions of these complexes form hydrogels when added to acid to lower the pH, and these hydrogels were used to prepare their corresponding xerogels, cryogels, and aerogels. Solvent exchange with ethanol and supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) drying of the starch gels preserved the structure of the gels and yielded aerogels having a macroporous nanoparticulate internal structure. Depressurization rates during SC-CO2 drying were examined to optimize aerogel properties, and starch aerogels with densities between 0.120–0.185 g cm−3 and BET surface areas ranging between 313–362 m2 g−1 were obtained. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), were used to characterize the aerogels. The corresponding xerogels and cryogels had inferior properties. This method provides an alternative method for the preparation of starch aerogels and eliminates many difficulties associated with starch gelatinization and retrogradation procedures that are currently used to prepare the prerequisite starch gels.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...