Supported protic acid-catalyzed synthesis of 2,3-disubstituted thiazolidin-4-ones: enhancement of the catalytic potential of protic acid by adsorption on solid supports†
Abstract
The catalytic potential of various protic acids has been assessed for the one pot tandem condensation–cyclisation reaction involving an aldehyde, an amine, and thioglycolic acid to form 2,3-disubstituted thiazolidin-4-ones. The catalytic potential of the various protic acids that follows the order TfOH > HClO4 > H2SO4 ∼ p-TsOH > MsOH ∼ HBF4 > TFA ∼ AcOH is improved significantly by adsorption on solid supports, in particular using silica gel (230–400 mesh size), with the resulting relative catalytic potential following the order HClO4–SiO2 > TfOH–SiO2 ≫ H2SO4–SiO2 > p-TsOH–SiO2 > MsOH–SiO2 ∼ HBF4–SiO2 > TFA–SiO2 ∼ HOAc–SiO2. The better catalytic potential of HClO4–SiO2 as compared to that of Tf–SiO2, although TfOH is a stronger protic acid than HClO4, can be rationalised through a transition state model depicting the interaction of the individual protic acid with SiO2. The catalytic efficiency of HClO4 adsorbed on various solid supports was in the order HClO4–SiO2 ≫ HClO4–K10 > HClO4–KSF > HClO4–TiO2 ∼ HClO4–Al2O3. The catalytic system HClO4–SiO2 is compatible with different variations of aldehydes (aryl/heteroaryl/alkyl/cycloalkyl) and the amines (aryl/heteroaryl/arylalkyl/alkyl/cycloalkyl) affording the desired 2,3-disubstituted thiazolidin-4-ones in 70–87% yields (43 examples). The electronic and the steric factors associated with the aldehydes and the amines provide a handle for selective thiazolidinone formation and were found to be dependent on the extent of imine formation. No significant amount of thiazolidinone formation took place during the reaction of the preformed amide (synthesised from the amine and thioglycolic acid) with benzaldehyde suggesting that the reaction proceeds through the initial reversible imine formation followed by cyclocondensation of the preformed imine with thioglycolic acid, the reversible imine formation being the determining step to control selectivity of thiazolidinone formation in competitive environments. The feasibility of a large scale reaction and catalyst recycling/reuse is demonstrated.
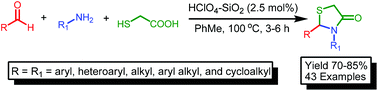

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...