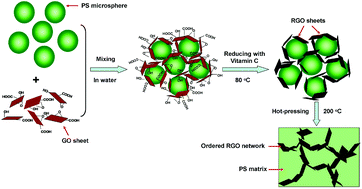
In this work, we report a new approach to resolve a practical problem in producing conductive polystyrene/reduced-graphene-oxide (PS/RGO) composites, i.e. the dilemma that raising the conductivity detrimentally compromises the environmental friendliness of the process because the prevalent chemistry designs emphasize raising conductivity in RGO production by employing strong and toxic chemicals or energy-consuming heat treatments. These designs then rely on organic solvents, chemical functionalization, and stabilizers to overcome the difficulty in dispersing and incorporating RGO into the polymer matrix. In our new design, we emphasize that a compact percolated three-dimensional microcellular RGO network with long-range order is the most effective use of RGO for high composite conductivity. With this guide, GO and non-polar PS mono-dispersed microspheres are co-dispersed in water, with GO stably adsorbing on the microspheres. PS/GO microspheres are then reduced with a nontoxic reducing agent such as vitamin C. PS/RGO microspheres are subsequently hot-pressed into a composite with the required compact percolated three-dimensional microcellular RGO structure. Experimental data collected from the resultant composites validate the design and indeed show low percolation threshold (0.08 vol%), high conductivity (20.5 S m−1), and good compliance with the principles of green chemistry.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...