Milk protein hydrolysates activate 5-HT2Cserotonin receptors: influence of the starting substrate and isolation of bioactive fractions
Abstract
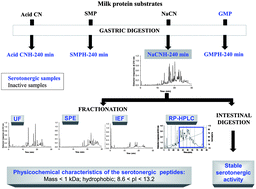
Milk
* Corresponding authors
a
Department of Life Sciences and Food for Health Ireland (FHI), University of Limerick, Castletroy, Limerick, Ireland
E-mail:
dick.fitzgerald@ul.ie
Fax: + 353 (0) 61 331490
Tel: +353 (0) 61 202598
b Food for Health Ireland, University College Cork, Cork, Ireland
c School of Pharmacy, University College Cork, Cork, Ireland
d Laboratory of Neurogastroenterology, Alimentary Pharmabiotic Centre, University College Cork, Cork, Ireland
e Department of Psychiatry, University College Cork, Cork, Ireland
f Department of Anatomy and Neuroscience, University College Cork, Cork, Ireland
Milk

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
A. B. Nongonierma, H. Schellekens, T. G. Dinan, J. F. Cryan and R. J. FitzGerald, Food Funct., 2013, 4, 728 DOI: 10.1039/C3FO30309H
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
