Egg intake improves carotenoid status by increasing plasma HDL cholesterol in adults with metabolic syndrome†
Abstract
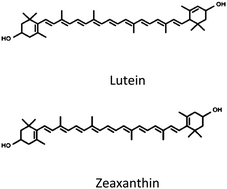
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is associated with reductions in plasma lutein and zeaxanthin, along with altered composition of their lipoprotein transporters which may affect disease risk. Egg yolk intake has been demonstrated to increase plasma lutein and zeaxanthin in other populations. The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of whole egg feeding on plasma and lipoprotein carotenoids in participants with MetS. Participants consumed 3 whole eggs per day (EGG, n = 20) or the equivalent amount of yolk-free egg substitute (SUB, n = 17), as part of a carbohydrate-restricted diet (CRD) for 12 weeks. Post-intervention, the EGG group had significant increases in plasma lutein (+21%), zeaxanthin (+48%), and β-carotene (+24%), while the SUB group had increases in plasma β-carotene (+55%) only. Significant enrichment of isolated HDL and LDL fractions in lutein (+20% HDL, +9% LDL) and zeaxanthin (+57% HDL, +46% LDL) was observed in the EGG group after 12 weeks. Increases in the proportion of plasma carotenoids carried by HDL was seen for lutein (P < 0.01), zeaxanthin (P < 0.01), β-cryptoxanthin (P < 0.05), and lycopene (P < 0.05) for all participants after the 12 week intervention. Daily intake of 3 whole eggs, as part of a CRD, increased both plasma and lipoprotein lutein and zeaxanthin. Egg yolk may represent an important food source to improve plasma carotenoid status in a population at high risk for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...