Organic pollutant levels in an agricultural watershed: the importance of analyzing multiple matrices for assessing streamwater pollution
Abstract
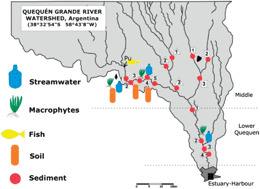
This study is aimed at analyzing the occurrence and transport of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in the Quequén Grande river basin, as representative of a catchment under diffuse pollution sources. Pollutant levels in soils, river bottom sediments (RBS), streamwater (Sw), suspended particle materials (SPMs), macrophytes and muscle of silverside were determined by GC-ECD. Soil Kd values for the current-used insecticides, endosulfans and cypermethrin, were established. Total levels (ng g−1 dry weight) in soil ranged between 0.07–0.9 for OCPs, 0.03–0.37 for PCBs and 0.01–0.05 for PBDEs. Endosulfan insecticide (α- + β- + sulfate metabolite) represented up to 72.5% of OCPs. The low soil retention for α-endosulfan (Kd: 77) and endosulfan sulfate (Kd: 100) allows their transport to Sw, SPM and RBS. Levels of endosulfan in Sw in some cases exceeded the value postulated by international guidelines for aquatic biota protection (3 ng L−1). PCB and PBDE pollution was related to harbour, dumping sites and pile tire burning. Tri and hexa PCB congeners predominated in all matrices and exceeded the quality guideline value of 0.04 ng L−1 in Sw. Considering levels in silverside muscle, none of the oral reference doses were exceeded, however, PCBs accounted for 18.6% of the total daily allowed ingest for a 70 kg individual. Although the levels of PCBs and OCPs in soil and RBS were low and did not go beyond quality guidelines, these compounds could still represent a risk to aquatic biota and human beings, and thus actions towards preventing this situation should be undertaken.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...