Highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen generation by solution-processed ZnO/Pt/CdS, ZnO/Pt/Cd1−xZnxS and ZnO/Pt/CdS1−xSex hybrid nanostructures†
Abstract
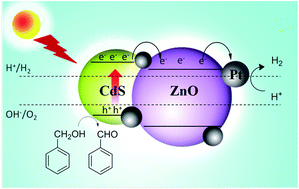
Photocatalytic generation of hydrogen by using the hybrid nanostructures, ZnO/Pt/CdS, ZnO/Pt/Cd1−xZnxS and ZnO/Pt/CdS1−xSex, has been studied under UV-visible and visible irradiation by employing Na2S and Na2SO3 as hole scavengers. Good H2 evolution rates up to 17.4 mmol h−1 g−1 and an apparent quantum yield (AQY) of 11.1% were obtained with ZnO/Pt/CdS under UV-visible irradiation. With the visible irradiation alone, the rate of H2 production was slower. With 20% Zn substitution in place of Cd in CdS, the rate of H2 generation was 31.2 mmol h−1 g−1 and 12.5 mmol h−1 g−1 respectively with UV-visible and visible irradiation, the corresponding AQY values being 23.1% and 18%. With 50% substitution of S by Se in CdS, the rate of hydrogen generation was at 19 mmol h−1 g−1 and 16 mmol h−1 g−1 with UV-visible and visible irradiation respectively, but the AQY values were in the range of 8–9%. Replacing Na2S and Na2SO3 by benzyl alcohol as the scavenger improves the catalytic activity of ZnO/Pt/CdS yielding H2 at the rate of 31.6 mmol h−1 g−1 and AQY of 34.5% under visible irradiation. The results were even more remarkable with ZnO/Pt/Cd0.8Zn0.2S where the rate was 36.5 mmol h−1 g−1 and the AQY reached 50.4% with visible irradiation. A noteworthy feature of the present study is that the hybrid nanostructures were prepared by simple solution processing involving sequential addition of reagents to ZnO nanoparticles in methanol medium.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...