Attaching high charge density metal ions to surfaces and biomolecules. Reaction chemistry of hypodentate cobalt diamine complexes†‡
Abstract
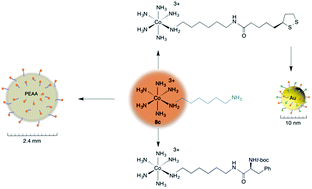
Hypodentate diamine cobalt(III) pentammine complexes [Co(NH3)5(NH2(CH2)nNH3)](ClO4)4 (8: a: n = 3; b: n = 4; c: n = 6; d: n = 8) have been synthesized via the reaction of [Co(NH3)5(OTf)](OTf)2 (TfOH = CF3SO3H) with the corresponding diamines. The analogous t-boc protected diamine complexes [Co(NH3)5(NH2(CH2)nNHt-boc)](ClO4)3 (7a–d) were prepared in 4–26% yield. Low yields for the formation of 7a–d are due to competing side reactions which also gave [Co(NH3)6]3+. Complexes 7a–d were deprotected using trifluoroacetic acid to give the corresponding hypodentate diamine complexes [Co(NH3)5(NH2(CH2)nNH3)](CF3CO2)0.5(ClO4)3.5 (9a–d). HBTU coupling of 8c with N-(t-boc)-L-phenylalanine gave an amino acid functionalized cobalt pentammine complex [Co(NH3)5(NH2(CH2)6NHt-boc)-L-phenylalanine)](ClO4)3 (10). All new complexes were characterized using UV-vis and 1H NMR spectroscopy, and elemental analysis. Grafting of 8c onto 2.4 mm poly(ethylene-co-acrylic acid) (PEAA) beads was achieved via amide coupling. Complex 8c was coupled to thioctic acid via amide coupling and the resulting cobalt disulfide complex [Co(NH3)5(N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanamide)](ClO4)3 (11) was attached to 10 nm Au nanoparticles. The amount of cobalt loading onto PEAA beads and Au nanoparticles was determined using ICP-MS and EDX.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...