Copper(ii) complexes with 2NO and 3N donor ligands: synthesis, structures and chemical nuclease and anticancer activities†
Abstract
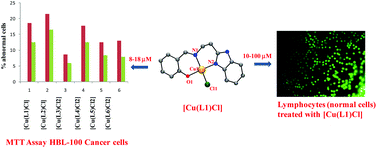
A series of water soluble copper(II) complexes of the types [Cu(L)Cl] 1–2, where LH is 2-(2-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)ethyliminomethyl)phenol (H(L1)), and 2-(2-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-ethyliminomethyl)-4-methylphenol (H(L2)), and [Cu(L)Cl2] 3–6, where L is (2-pyridin-2-yl-ethyl)pyridin-2-ylmethyleneamine (L3), 2-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)ethylpyridin-2-yl-methyleneamine (L4), 2-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)ethyl(1H-imidazol-2-ylmethylene)amine (L5), and 2-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)ethyl-(4,4a-dihydroquinolin-2-ylmethylene)amine (L6), have been isolated and characterized by elemental analysis, electronic absorption, ESI-MS and EPR spectral techniques and the electrochemical method. The single crystal X-ray structures of [Cu(L1)Cl] 1 and [Cu(L2)Cl] 2 possess a distorted square-based coordination geometry while [Cu(L4)Cl2] 4 and [Cu(L6)Cl2] 6 possess a distorted trigonal bipyramidal coordination geometry. Both absorption spectral titration and an EthBr displacement assay reveal that all the complexes bind with calf thymus (CT) DNA through covalent mode of DNA interaction involving the replacement of an easily removable chloride ion with DNA nucleobases. All the complexes exhibit oxidative cleavage of supercoiled (SC) plasmid DNA in the presence of hydrogen peroxide as an activator. It is remarkable that at 50 μM concentration 5 and 6 completely degrade SC DNA into undetectable minor fragments and thus they act as efficient chemical nucleases. All the complexes are remarkable in displaying cytotoxicity against the HBL-100 human breast cancer cell line with potency more than that of the widely used drug cisplatin and hence they have the potential to act as promising anticancer drugs. Interestingly, they are non-toxic to normal cell lymphocytes isolated from human blood samples, revealing that they are selective in killing only the cancer cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...