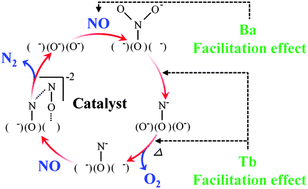
C-type cubic Y2O3, (Y0.70Tb0.30)2O3+δ, and (Y0.99−xTbxBa0.01)2O2.99+δ (x = 0, 0.10, 0.20, 0.30, and 0.40) were prepared to investigate their catalytic performance for NO decomposition. In the direct NO decomposition process, NO is adsorbed on basic sites of the catalyst surface to form adsorbed nitrosyl, and the number of basic sites affects the NO decomposition activity. In particular, the negative effect of CO2 presence on the catalytic activity is related to the number of the surface basic sites. Furthermore, it was evidenced from temperature programmed desorption (TPD) of NO and IR measurements that adsorbed nitrosyl reacts with gas-phase NO and decomposes to N2. The effects of Ba2+ and Tb3+/4+ introduction on the activity of the catalyst are discussed based on this NO reaction mechanism. It is concluded that the principal effects of Ba2+ doping are an increase in the number of basic sites and the generation of oxide anion vacancies in the lattice. In addition, we demonstrate that Tb3+/4+ ions in the lattice facilitate O2 desorption and act as NO adsorption sites, so that the catalytic activity is significantly enhanced by Tb3+/4+ introduction, despite the small number of basic sites on the catalyst surface.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...