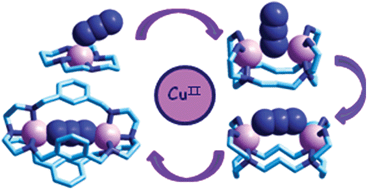
Alfred Werner's complexes of formula [MIII(NH3)6−nXn]X3−n involved inert metal centres (M = Cr, Co), and anions X− ‘frozen’ in the coordination sphere, a circumstance which allowed the isolation of a variety of isomers. Amine complexes of labile transition metal ions, studied later, do not form isomers, yet they allow the investigation of the fast and reversible interaction of the anion X− with the metal–amine core. On these bases, anion receptors of varying degrees of sophistication have been synthesised, which consist of coordinatively unsaturated polyamine metal complexes and whose vacant coordination sites can be occupied by anion donor atoms. A thoughtful design of the polyamine framework may introduce geometrical selectivity, resulting from the matching between anion shape and size and the geometrical features of receptor's cavity. Compared to their purely organic counterparts, metal containing receptors display several advantages: (i) metal–anion interactions are strong enough to more than compensate anion dehydration energy, which allows recognition studies to be carried out in water; (ii) transition metal ions of different electronic configurations exhibit different geometrical preferences, which addresses anion binding and introduces a further element of selectivity. Chosen examples of polyamine metal complexes, including macrocycles and cages, displaying selective binding tendencies towards anions will be illustrated in this tutorial review.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...