Peptides and peptidomimetics that behave as low molecular weight gelators
Abstract
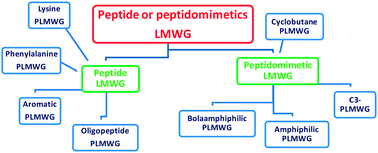
Gelators may be divided into chemical gels and physical gels: the internal structure of chemical gels is made of chemical bonds, while physical gels are characterized by dynamic cross-links that are constantly created and broken. The gelator present in physical gels may be an inorganic or an organic compound, the latter having a molecular weight of ≤500 amu. These compounds are generally called “low molecular weight gelators” (LMWGs). In this tutorial review we want to focus our attention on short peptides or peptidomimetics that behave as LMWGs. Peptidomimetics are small protein-like molecules designed to mimic natural peptides. To efficiently design a peptidomimetic, local constraints must be introduced into the skeleton, to induce the formation of preferred secondary structures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...