Simultaneous induction of high level thermal and visible-light catalytic activities to titanium(iv) oxide by surface modification with cobalt(iii) oxide clusters†
Abstract
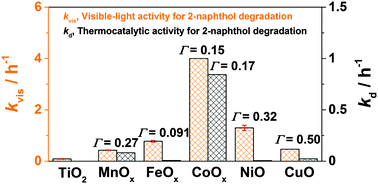
This study first presents a “TiO2-based eco-catalyst” working in the dark and under visible-light irradiation for the degradation of environmental organic pollutants. Molecular scale cobalt(III) oxide clusters are formed on the surface of highly active anatase TiO2 nanoparticles (Co2O3–TiO2) by the chemisorption–calcination cycle method. Co2O3–TiO2 exhibits very high visible-light activities for the degradation of 2-naphthol and formic acid used as model organic pollutants. Unprecedented thermocatalytic activity is concomitantly endowed on TiO2 by the surface modification. Prolonging reaction time in the Co2O3–TiO2 photo- and thermo-catalyzed reactions leads to the decomposition of 2-naphthol and formic acid to CO2. The essential action mechanisms of the Co2O3 clusters in the photocatalysis and thermocatalysis of Co2O3–TiO2 were discussed on the basis of spectroscopic and electrochemical data.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...