An in situ FTIR spectroscopic study of the electrochemical oxidation of ethanol at a Pb-modified polycrystalline Pt electrode immersed in aqueous KOH
Abstract
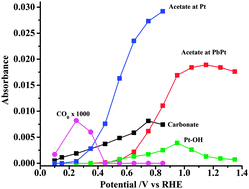
A study of the mechanism of ethanol oxidation in alkaline solution on a platinum electrode modified with an irreversibly-deposited layer of lead has been carried out using in situ FTIR spectroscopy. This study provides support for the suggestion that the adsorption mechanism of ethanol is substantially modified in the presence of Pb, with a carbon-bonded intermediate being favoured leading to facile scission of the C–C bond in ethanol. We have found that the formation of carbonate takes place at potentials close to the thermodynamic value. At higher potentials, when Pb is lost to solution, the mechanism of oxidation of ethanol reverts to that found on a normal polycrystalline Pt surface, with the primary product being acetate.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...